
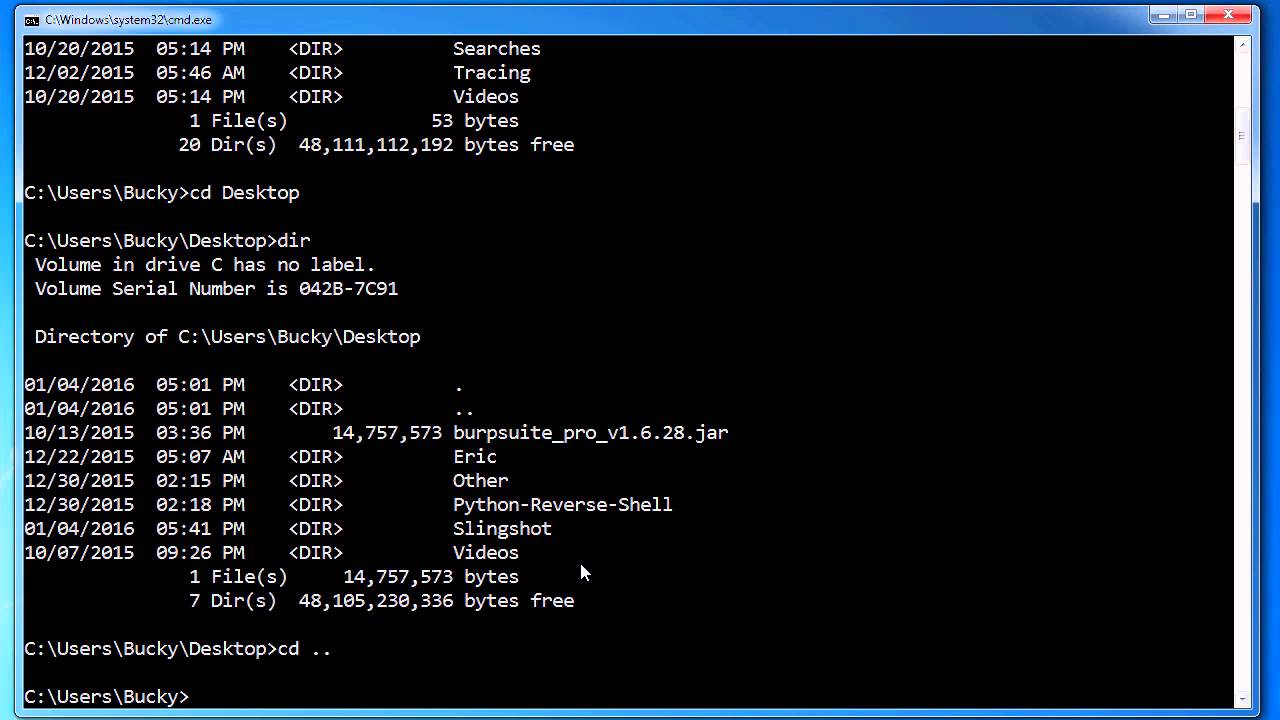
- #Python3.6 list directory contents how to
- #Python3.6 list directory contents install
- #Python3.6 list directory contents code
- #Python3.6 list directory contents download
prefix, like this: ()įor example: mkdir("New Folder") 🔹 Current Working Directory In this case, you can call the functions in your script as you normally would, without adding the os. įor example: from os import listdir, system
If you are only going to work with one or two functions from the module, you can import them individually using this syntax: from import,.
#Python3.6 list directory contents how to
before the name of the function that you want to call, like this: os.()įor example: os.mkdir("New Folder") How to Import Individual Functions To be able to use the functions from the os module, you will need to add the prefix os. 💡 Tip: this module was already installed when you installed Python 3, so you will be able to use it immediately. This will give you access to all the functions defined in the os module. To import the os module, you simply need to include this line at the top of your Python script or run this line in the interactive shell: import os
#Python3.6 list directory contents code
We import a module when we want to use its code in our script. Importing a module means gaining access to all the functions and variables that are stored within the module. To use the os module in your script, you need to "import" it. A module is a file that contains related Python code.An example of a directory is your "Documents" folder.
#Python3.6 list directory contents install
Procedure to install Virtual Environment for python3.If you want to learn how these functions work behind the scenes and how you can use their full power, then this article is for you. NOTE : Please ensure that all the packages(requirements mentioned below) are removed from the root folders as they might conflict with the packages of virtual environment. Install required repositories ON FEDORA 25.Install required repositories ON CENTOS 7 or RHEL 7.Install PIP3.6 for installing required packages: To run python3.6 on shell run the command:.To check the Python Version run the command: Python is now installed on your machine.Compile the extracted package and install (make altinstall will install the python3.6 package without disturbing the existing python2.7 that exists in most of the Linux distributions):.
#Python3.6 list directory contents download


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
